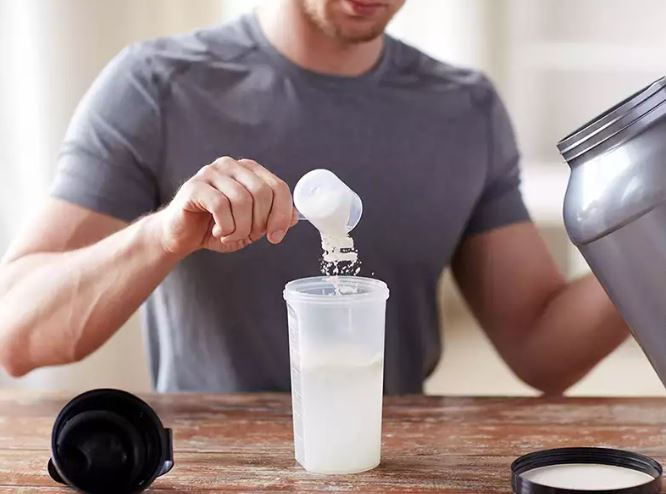
Protein has become the superstar of fitness nutrition, sparking endless debates about the best types, sources, and timing for consumption. Whether you’re team food-only, pro-supplementation, or somewhere in between, one thing is clear: protein is essential for building and maintaining muscle.
For busy parents juggling workouts with hectic schedules, understanding whey protein’s role and timing can make a big difference in fitness goals. Here’s what you need to know about incorporating whey protein into your routine effectively.
Types of Whey Protein: Know Your Options
Whey protein comes in various forms, each with its unique processing methods and benefits. Let’s break them down:
1. Whey Protein Concentrate
This is the least processed form of whey protein. While it’s more “natural,” it contains less pure protein (about 70-85%) and has more fat and lactose. If you’re not lactose-sensitive and prefer a cost-effective option, this could work for you.
2. Whey Protein Isolate
Isolate undergoes additional processing, resulting in higher protein content (90% or more) and less fat and lactose. It’s ideal for those with mild lactose intolerance and those seeking a leaner supplement.
3. Hydrolyzed Whey Protein
Hydrolyzed whey is pre-digested into smaller amino acid chains for potentially faster absorption. While marketed as superior, studies show it offers no significant advantage over other types, so save your budget unless you have specific digestive concerns.
Regardless of the type you choose, whey protein effectively supports muscle recovery and growth when consumed at the right time.
Timing: When Should You Take Whey Protein?
Whey protein is highly bioavailable, meaning your body can absorb it quickly, making it perfect for post-workout recovery.
When you exercise, your muscles experience micro-tears, and rebuilding them during recovery leads to strength and growth. Immediately after your workout, your muscles act like a sponge, ready to absorb nutrients.
Why post-workout is ideal:
- Whey protein delivers essential amino acids quickly.
- Blood flow to muscles increases after exercise, enhancing nutrient delivery.
- You transition your muscles from a catabolic (breakdown) state to an anabolic (growth) state.
The “anabolic window”:
For maximum benefit, consume whey protein within two hours of your workout. While the sooner, the better, aim not to delay too long, as your muscles’ ability to absorb nutrients diminishes over time.
Who Should Consider Whey Protein?
Whey protein is a convenient, affordable option for active individuals and busy parents who need quick post-workout nutrition. While it’s possible to meet protein needs through food alone, this isn’t always practical when life gets in the way.
For example:
- Your workout ends minutes before school drop-off or a meeting.
- You don’t have time to prepare or eat a balanced meal post-workout.
Whey protein powders, shakes, or bars can be lifesavers when every minute counts.
Protein needs for active individuals:
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) suggests 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight—sufficient for sedentary people. Active adults, however, benefit from 1.2 to 1.6 grams per kilogram, especially when building muscle or recovering from injury.
While whey protein fits seamlessly into most routines, it’s not for everyone. Vegans and those with severe lactose intolerance may prefer plant-based options like hemp or pea protein.
Final Thoughts
For busy parents aiming to stay fit and healthy, whey protein can be a valuable ally. Its convenience and effectiveness make it a smart choice for anyone juggling family, work, and fitness goals. Whether you opt for concentrate, isolate, or a different protein altogether, focus on timing your intake for optimal results.
With whey protein in your corner, you can fuel your recovery and reach your goals—all while keeping up with the kids!

Subscribe To Our VIP Newsletter
Join our VIP mailing list to receive additional content that goes even deeper into the latest tips to ensure you and your families health, fitness and wellness.