When done properly, stretching can do more than just increase flexibility. Benefits of stretching include:
- enhanced physical fitness
- enhanced ability to learn and perform skilled movements
- increased mental and physical relaxation
- enhanced development of body awareness
- reduced risk of injury to joints, muscles, and tendons
- reduced muscular soreness
- reduced muscular tension
- increased suppleness due to stimulation of the production of chemicals which lubricate connective tissues
- reduced severity of painful menstruation (dysmenorrhea) in females
Unfortunately, even those who stretch do not always stretch properly and hence do not reap some or all of these benefits. Some of the most common mistakes made when stretching are:
- improper warm-up
- inadequate rest between workouts
- overstretching
- performing the wrong exercises
- performing exercises in the wrong (or sub-optimal) sequence
Warming Up
Stretching is not warming up! It is, however, a very important part of warming up. Warming up is quite literally the process of “warming up” (i.e., raising your core body temperature). A proper warm-up should raise your body temperature by one or two degrees Celsius and is divided into two phases:
Warming up is quite literally the process of “warming up” (i.e., raising your core body temperature). A proper warm-up should raise your body temperature by one or two degrees Celsius and is divided into two phases:
- general warm-up
- stretching
It is very important that you perform the general warm-up before you stretch. It is not a good idea to attempt to stretch before your muscles are warm (something which the general warm-up accomplishes).
Warming up can do more than just loosen stiff muscles; when done properly, it can actually improve performance. On the other hand, an improper warm-up, or no warm-up at all, can greatly increase your risk of injury from engaging in athletic activities.
It is important to note that active stretches and isometric stretches should not be part of your warm-up because they are often counterproductive. The goals of the warm-up are an increased awareness, improved coordination, improved elasticity and contractibility of muscles, and a greater efficiency of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
Active stretches and isometric stretches do not help achieve these goals because they are likely to cause the stretched muscles to be too tired to properly perform the athletic activity for which you are preparing your body.
General Warm-Up
The general warm-up is divided into two parts:
- joint rotations
- aerobic activity
These two activities should be performed in the order specified above.
Joint Rotations
The general warm-up should begin with joint-rotations, starting either from your toes and working your way up, or from your fingers and working your way down. This facilitates joint motion by lubricating the entire joint with synovial fluid. Such lubrication permits your joints to function more easily when called upon to participate in your athletic activity.
You should perform slow circular movements, both clockwise and counter-clockwise, until the joint seems to move smoothly. You should rotate the following (in the order given, or in the reverse order):
- fingers and knuckles
- wrists
- elbows
- shoulders
- neck
- trunk/waist
- hips
- legs
- knees
- ankles
- toes
Aerobic Activity
After you have performed the joint rotations, you should engage in at least five minutes of aerobic activity such as jogging, jumping rope, or any other activity that will cause a similar increase in your cardiovascular output (i.e., get your blood pumping).
The purpose of this is to raise your core body temperature and get your blood flowing. Increased blood flow in the muscles improves muscle performance and flexibility and reduces the likelihood of injury.
Warm-Up Stretching
The stretching phase of your warmup should consist of two parts:
- static stretching
- dynamic stretching
It is important that static stretches be performed before any dynamic stretches in your warm-up.
Dynamic stretching can often result in overstretching, which damages the muscles. Performing static stretches first will help reduce this risk of injury.
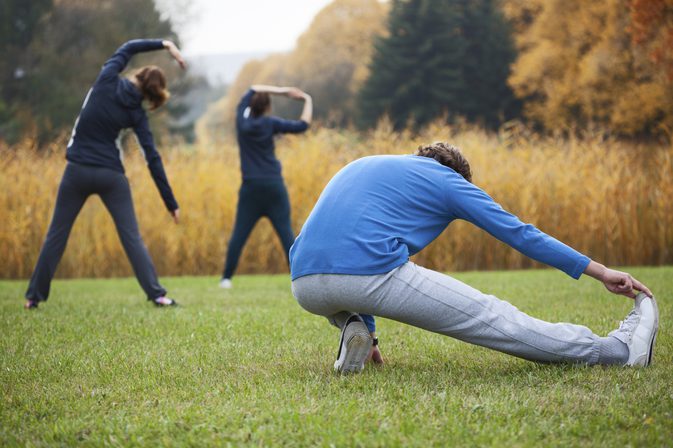

Static Warm-Up Stretching
Once the general warm-up has been completed, the muscles are warmer and more elastic. Immediately following your general warm-up, you should engage in some slow, relaxed, static stretching.
You should start with your back, followed by your upper body and lower body, stretching your muscles in the following order:
- back
- sides (external obliques)
- neck
- forearms and wrists
- triceps
- chest
- buttocks
- groin (adductors)
- thighs (quadriceps and abductors)
- calves
- shins
- hamstrings
- instep
Some good static stretches for these various muscles may be found in most books about stretching. Unfortunately, not everyone has the time to stretch all these muscles before a workout. If you are one such person, you should at least take the time to stretch all the muscles that will be heavily used during your workout.
Dynamic Warm-Up Stretching
Once you have performed your static stretches, you should engage in some light dynamic stretching: leg-raises, and arm-swings in all directions. You should do as many sets as it takes to reach your maximum range of motion in any given direction, but do not work your muscles to the point of fatigue.
Remember — this is just a warm-up, the real workout comes later. Some people are surprised to find that dynamic stretching has a place in the warm-up. But think about it: you are “warming up” for a workout that is (usually) going to involve a lot of dynamic activity. It makes sense that you should perform some dynamic exercises to increase your dynamic flexibility.
Cooling Down
Stretching is not a legitimate means of cooling down. It is only part of the process. After you have completed your workout, the best way to reduce muscle fatigue and soreness (caused by the production of lactic acid from your maximal or near-maximal muscle exertion) is to perform a light warm-down.
This warm-down is similar to the second half of your warm-up (but in the reverse order).
The warm-down consists of the following phases:
- dynamic stretching
- static stretching
First perform some light dynamic stretches until your heart rate slows down to its normal rate, then perform some static stretches. Stretching can reduce cramping, tightening, and soreness in fatigued muscles and will make you feel better.
Light warm-down exercise immediately following maximal exertion is a better way of clearing lactic acid from the blood than complete rest.
Furthermore, if you are still sore the next day, a light warm-up or warm-down is a good way to reduce lingering muscle tightness and soreness even when not performed immediately after a workout.

Subscribe To Our VIP Newsletter
Join our VIP mailing list to receive additional content that goes even deeper into the latest tips to ensure you and your families health, fitness and wellness.